What is spot welding? What Is Spot Welding Used For?
What Is Spot Welding?
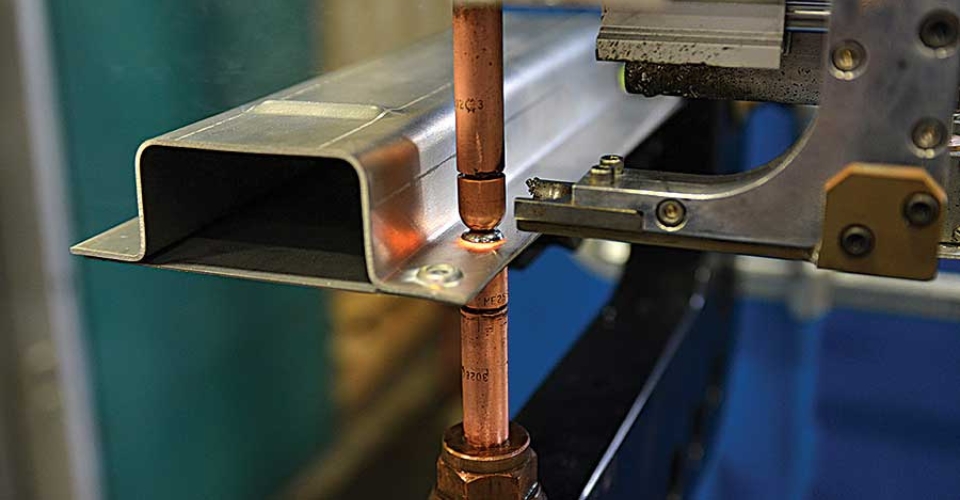
Spot welding is a resistance welding process used primarily to weld two or more metal sheets together. It is achieved by applying pressure and electric current to the spot-weld area. The required heat is generated by the metal’s internal resistance to the electric current.
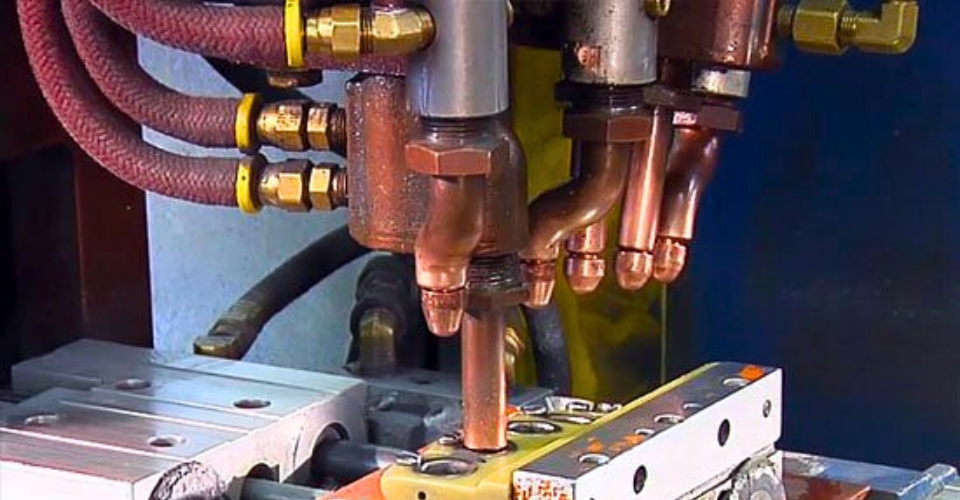
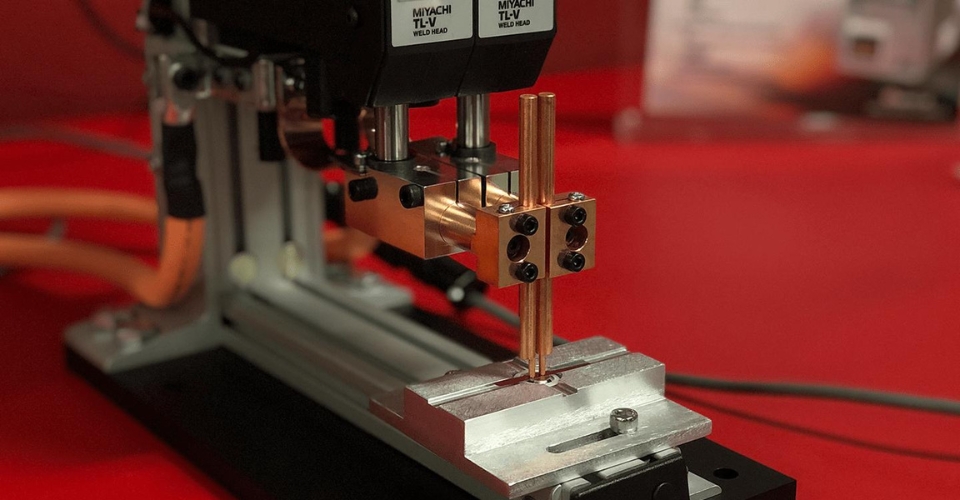
The electric current and pressure are applied by copper alloy electrodes whose tips are placed on the opposite sides of the metal pieces. The generated heat melts the metal while the pressure from the electrodes squeezes the molten metal to form a weld.
It’s called spot welding because this welding method creates a tiny dot weld, that looks like a spot. The weld created between the copper electrodes is also sometimes called a nugget.
What Is Spot Welding Used For?
Spot welding is used to join electricity-conducting sheet metal and wire meshes. Its typically used to weld thin metals but thicknesses above 1 in. are possible only with specialized heavy-duty equipment.
It’s mostly used to manufacture automobiles. A single-vehicle typically has over 1000 spot welds over its body panels. This is done with spot welding robots in a matter of seconds. But sheet metal shops use less sophisticated methods when working on a car body.
Resistance spot welding is also used in industries like aerospace, rail, manufacturing, electronics, construction, battery, and others. It’s almost universal that spot welding robots complete this welding process in an industrial setting.
A manual spot welding machine is a useful addition to any welding shop. While not automated, it can help you create complex shapes with less effort compared to TIG or MIG welding. Besides, most jobs that require a resistance spot weld are difficult to complete without it.
Pros of Spot welding tips
- Resistance spot welding allows for high energy delivery to a concentrated spot in a short time
- Welds any conductive metal
- It’s relatively easy to perform – reduces the required operator’s skill
- Saves time and effort compared to other welding processes
- Best method to achieve proper weld strength with thin metal without burning through
- Many spot welding electrodes types are available for welding different metal alloys
- Allows for swift and efficient welds
- Electrodes handle the thermal conductivity problem by dissipating the heat away from the spot weld
- Resistance welding creates controlled, repeatable welds
- It’s a proven and time tested welding process with lots of literature available
- Welding current use is highly efficient
Cons of Spot welding tips
- You can’t spot weld metal if one side is not accessible
- Resistance spot welding may harden the nugget and the material around it, leading to cracks
- It can affect the chemical and physical properties of the workpiece metal. Corrosion resistance may be compromised with stainless steel, aluminum, and other metals
- It outputs tiny voltages (1-20V). So, any fluctuation can influence the spot weld quality
- Depending on the metal type and thickness, it may require frequent repairs